In the digital age, network ports serve as communication gateways, enabling data transfer between devices across the internet or private networks. Understanding these ports and their functions is essential for IT professionals, network administrators, and cybersecurity experts. In this guide, we’ll explore common network ports and their primary uses.
What Are Network Ports?
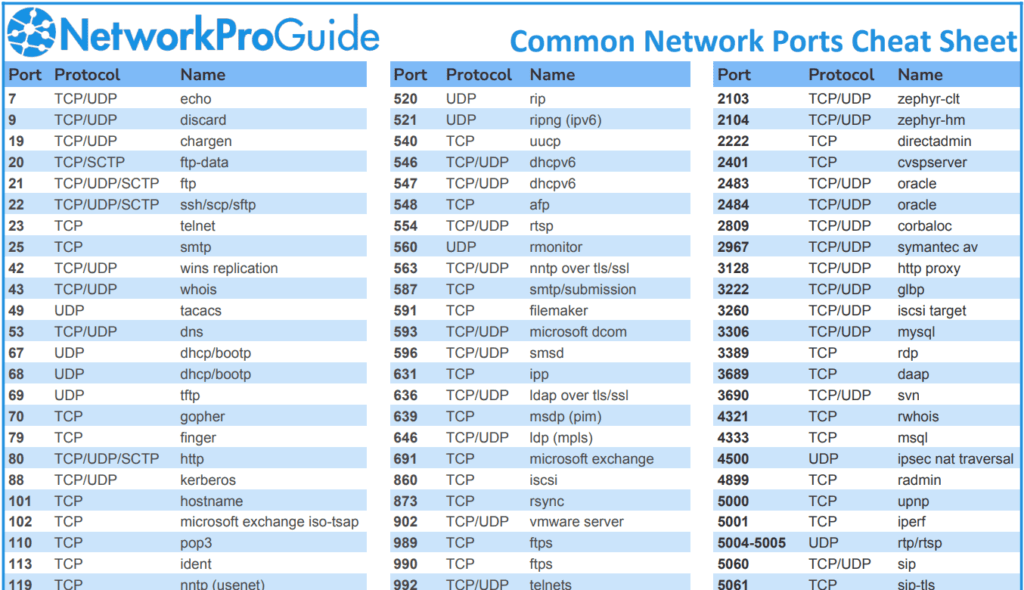
A network port is a virtual endpoint that facilitates communication between devices over a network. Ports are associated with IP addresses and are managed by the transport layer of the OSI model, primarily through the TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
Ports are identified by numbers ranging from 0 to 65535 and are categorized as:
- Well-Known Ports (0-1023): Reserved for standard services and protocols.
- Registered Ports (1024-49151): Used by software applications.
- Dynamic/Private Ports (49152-65535): Assigned dynamically for temporary purposes.
Commonly Used Network Ports
1. Port 20 and 21 – File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Purpose: Transfers files between a client and server.
- Details:
- Port 20: Handles data transfer.
- Port 21: Manages the control connection.
- Usage: Website hosting, file sharing.
2. Port 22 – Secure Shell (SSH)
- Purpose: Provides secure remote login and command execution.
- Details: Encrypts communication to prevent unauthorized access.
- Usage: Managing servers and secure file transfer via SCP or SFTP.
3. Port 23 – Telnet
- Purpose: Facilitates unencrypted remote access.
- Details: Considered insecure; replaced by SSH in most cases.
- Usage: Legacy systems, network troubleshooting.
4. Port 25 – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- Purpose: Sends emails between servers.
- Details: Often replaced by port 587 or 465 for secure connections.
- Usage: Email servers and applications.
5. Port 53 – Domain Name System (DNS)
- Purpose: Translates domain names into IP addresses.
- Details: Supports both TCP and UDP.
- Usage: Internet browsing, hosting services.
6. Port 80 – HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Purpose: Enables communication between web browsers and servers.
- Details: Non-secure; often replaced by HTTPS on port 443.
- Usage: Accessing websites.
7. Port 110 – Post Office Protocol (POP3)
- Purpose: Retrieves emails from a server.
- Details: Not encrypted; often replaced by IMAP or secured POP3.
- Usage: Email clients.
8. Port 143 – Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
- Purpose: Manages and retrieves emails while keeping them on the server.
- Details: Supports folder synchronization.
- Usage: Modern email systems.
9. Port 443 – HTTP Secure (HTTPS)
- Purpose: Secures communication over HTTP using SSL/TLS encryption.
- Details: Widely used for secure web browsing.
- Usage: Online shopping, banking, and secure data transfer.
10. Port 3389 – Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
- Purpose: Allows remote control of Windows computers.
- Details: Encrypted communication for security.
- Usage: IT support, remote access.
Why Are Network Ports Important?
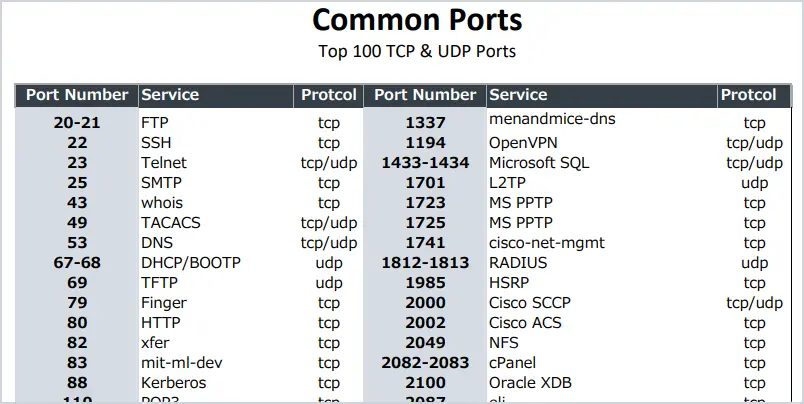
Understanding network ports helps in:
- Enhancing Security: Identifying vulnerabilities like open ports.
- Optimizing Network Performance: Configuring Port Forwarding and Firewalls.
- Troubleshooting Issues: Diagnosing connectivity problems.
Conclusion
Network ports are critical for seamless communication in modern computing. Familiarity with these ports enhances your ability to manage networks effectively and ensures secure data transmission. Stay updated with network protocols and port configurations to maintain robust IT infrastructure.
FAQs
What are network ports used for?
They enable communication between devices over a network.
Which ports are commonly used?
Ports 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), and 53 (DNS) are widely used.
How do ports improve security?
Managing ports helps prevent unauthorized access and enhances firewall protection.



